Isoabsorptive Point Method for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol and Orphenadrine Citrate in Their Combined Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
A B S T R A C T
A simple, specific, accurate and precise spectrophotometric method was settled for simultaneous determination of paracetamol and orphenadrine citrate in their pure form and in their pharmaceutical formulation. Isoabsorptive point technique has been used in simultaneous determination of both drugs without prior separation. Isoabsorptive point method parameters were validated according to ICH guidelines in which accuracy, precision, repeatability and robustness were found in accepted limits. Advantages and disadvantages of Isoabsorptive point were discussed and statistical comparison between the proposed method and the reference one was also performed.
Keywords
Spectrophotometric, Paracetamol, Orphenadrine, isoabsorptive point, ICH guidelines
Introduction
Paracetamol (PAR); N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide (Figure 1) is related to a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) which acts centrally and peripherally for treatment of non-inflammatory conditions in patients with gastric symptoms [1]. Orphenadrine citrate (ORP); (±)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(o-methyl-a-phenylbenzyl) oxy] ethylamine citrate (Figure 1) is a skeletal muscle relaxant which acts centrally by depressing a specific neurons in the nervous system so that impulses of the somatic nerves can’t be generated [1]. The combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and a skeletal muscle relaxant is better than single agents alone [2]. ORP can be used in combination with PAR as it prolongs and increases its antinociceptive effect [1]. The literature revealed that several methods have been carried out for the analysis of PAR and ORP in their mixture form or in their combination with other drugs. PAR & ORP were determined by spectrophotometric methods, HPLC methods, TLC and microemulsion HPLC method and square wave voltammetric method [1, 3-13]. To the best of our knowledge, there is no reported method for the determination of this drug mixture using Isoabsorptive point technique. As such, the aim of work is to develop a spectrophotometric method which is accurate, fast and non-complicated for determination of PAR & ORP combination without the interference of their additives or their excipients in pharmaceutical formulations.
Figure 1: Chemical structures of paracetamol (PAR) and orphenadrine citrate (ORP).
Experiment
I Apparatus
JASCO dual beam UV-visible spectrophotometer model V-630 (Japan), connected to an ACER compatible computer with spectra manager II software was used. The spectral slit width was 2 nm and it could scan at speed up to 8000 nm/min. All the measurements were carried out in 1 cm quartz cell over wavelength range of 200-400 nm at room temperature.
II Materials and Reagents
i Pure Standards
PAR and ORP were obtained as a gift from Egyptian International Pharmaceutical Industries Co. (EIPICO), located in 10th of Ramadan city, Egypt. Their purity was reported to be 99.50% and 99.70%, respectively.
ii Pharmaceutical Formulations
Orphenadrine plus® tablets were obtained from the market (label claim: Orphenadrine citrate 50 mg and Paracetamol 450 mg) manufactured by Alexandria Co., Egypt.
iii Solvents
HPLC grade Methanol was obtained from LiChrosolv, Merck KGaA, 64271 Darmstadt Germany. All of measurements were carried out by using 90% Methanol (HPLC grade methanol: Distilled water 9:1).
iv Standard Solutions
PAR and ORP stock standard solutions of 1 mg/mL were prepared in 90% methanol. PAR working standard solutions of 40 µg/mL were prepared in 90% methanol while ORP working standard solutions of 50 µg/mL were prepared by dilution from the stock solution with 90% methanol.
v Laboratory Prepared Mixtures
Solutions of different ratios of PAR & ORP were prepared by transferring accurate aliquots from their standard solutions to 10 mL volumetric flasks and then diluting with 90% methanol.
III Procedure
i Construction of Calibration Curves
For PAR, Working solutions equivalent to (4-22 µg/mL) were prepared by adding aliquots (1, 1.50, 2, 2.50, 3, 3.50, 4, 4.50, 5, 5.50 mL) of PAR working standard solution (40 µg/mL) to a series of 10 mL volumetric flasks and diluting with 90% methanol. For ORP, Working solutions equivalent to (5-50 µg/mL) were prepared by adding aliquots (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 mL) of ORP working standard solution (50 µg/mL) to a series of 10 mL volumetric flasks and diluting with 90% methanol. The absorption spectra were measured at room temperature over the wavelength (200-400 nm) for all measurements.
For Isoabsorptive Point Method
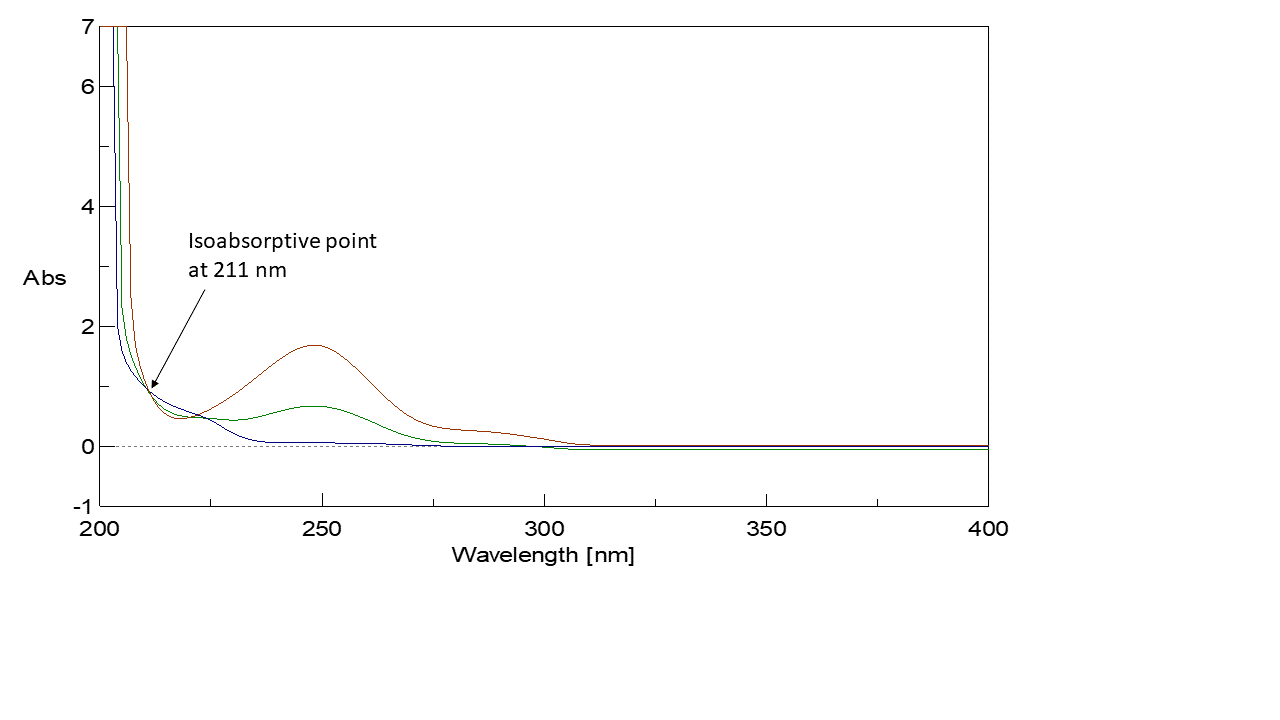
A calibration curve was constructed relating absorbance of the zero-order spectra of PAR at 𝜆 = 280 nm (Plateau region of ORP in which its absorbance is zero) and the zero-order spectra of PAR and ORP at 𝜆 = 211 nm (Isoabsorptive point) to their corresponding concentrations in 𝜇g/mL (Figure 2, 3) then the regression equation was computed. For PAR quantitation, Plateau region (𝜆 = 280 nm) was applied for estimation of the concentration of PAR. For ORP quantitation, isoabsorptive method was applied for estimation of total concentration of PAR and ORP. Absorption spectra of 20 𝜇g/mL of PAR, of 20 𝜇g/mL of ORP, and of a mixture containing 10 𝜇g/mL of each of PAR and ORP displayed isoabsorptive point at 211 nm point in the absorption spectrum, the total concentration of PAR and ORP in the mixture could be determined and consequently ORP concentration was calculated by subtraction of PAR concentrations. The total concentration of PAR and ORP could be calculated using the following equation:
𝐴211 = 0.0485𝐶 + 0.0427 (r=0.9994).
where 𝐶 represents the concentration of total concentration of PAR and ORP in 𝜇g/mL, 𝐴 represents the absorbance of PAR or ORP at 211 nm, and 𝑟 represents the correlation coefficient. The major limitation of this method is that it needs a plateau region or a complementary analytical method for determination of one of the analytes in the mixture.
Figure 2: Zero absorption spectrum of 20 µg/mL OPR overlaid with 20 µg/mL PAR and a mixture of 10 µg/mL ORP & 10 µg/mL PAR revealed that 211 nm is an isoabsorptive point and that ORP has no absorbance at 280 nm.
Figure 3: Zero absorption spectra of PAR overlaid with zero absorption spectra of ORP.
ii Analysis of Laboratory Prepared Mixtures
After preparation of different ratios of laboratory prepared mixtures, the spectra of these mixtures were measured and treated in the same way as described under the proposed methods.
iii Application to Pharmaceutical Formulation
10 Tablets of Orphenadrine plus® were weighed and crushed then an amount equivalent to 50 mg PAR and 5.55 mg ORP in each tablet was transferred into a 50 mL volumetric flask and diluted with 90% methanol as follows: First, 30 mL of 90% methanol were added and sonicated then dilution was carried out to the mark and filtered. Second, 10 mL of the dilution was transferred into a 100 mL volumetric flask to give a concentration equivalent to 100 µg/mL PAR and 11.11 µg/mL ORP. Third, any further dilutions were done in 10 mL volumetric flasks and treated in the same way as described under the proposed methods.
Results and Discussion
I Method Optimization
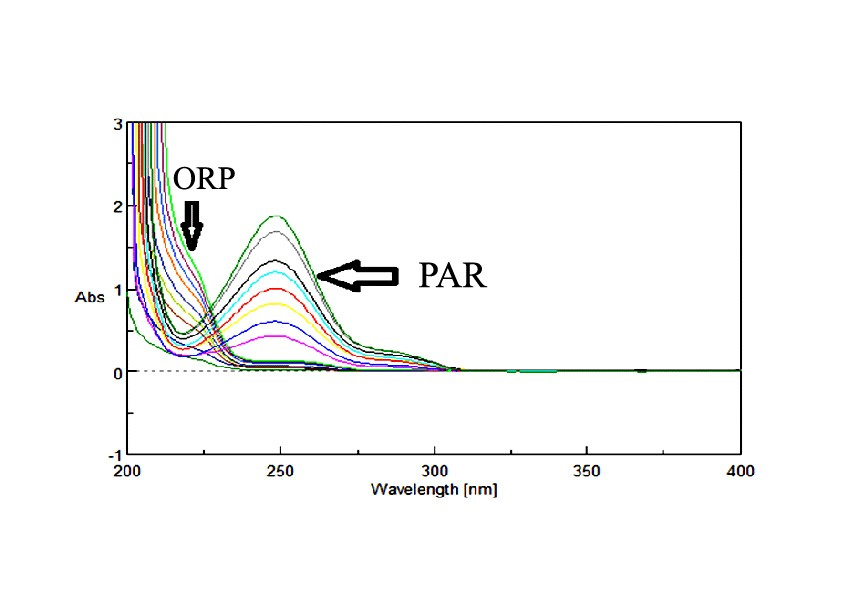
Two major problems were found during the analysis of PAR & ORP binary mixture; first, the overlapped spectra between the absorptivities of the drugs, and second, PAR, the major constituent in the dosage forms, had unfortunately high absorbance, while ORP the minor component in the dosage forms, had low absorbance values. As such, sample enrichment technique was used in which the concentration of the minor component ORP in its binary mixture was increased to facilitate its determination [14]. This was done by the addition of fixed amount of standard ORP to each experiment when combined with PAR, then subtracting its concentration before calculating the claimed concentration of the drug. Sample enrichment technique was used to solve the same problem for analyzing other drug mixtures of different drug ratios [15, 16] .
Isoabsorptive Point Method
211 and 280 nm absorbances were used for determination of PAR & ORP in presence of each other. The calibration curves revealed accepted linear relationships between concentrations and absorbance in a range of 4-22 µg/mL for PAR and 5-50 µg/mL for ORP with correlation coefficients of ≥ 0.9990 for both drugs. The accuracy of the method illustrated accepted values with 100.36% ± 1.08 for PAR and 101.41% ± 0.59 for ORP. The specificity of the methods demonstrated accepted values with 100.17% ± 1.02 for PAR and 100.85% ± 1.20 for ORP. The results are detailed in (Table 1). Isoabsorptive point is very easy and simple as it depends on zero absorption spectra without the need of extra processing. On the other hand, it has two limitations; one is the need for some specific calculations to determine the values of Isoabsorptive point and the other is requiring more time for performing the standard addition on each mixture.
Table 1: Assay parameters and validation results obtained by applying Isoabsorptive assay spectrophotometric method.
|
Mixture |
PAR & ORP |
|
|
Method Parameters |
ORP |
PAR |
|
Wavelength (nm) |
211 |
280 |
|
Linearity range (µg/mL) (n=3) |
5-50 |
4-22 |
|
Intercept |
0.0427 |
0.0070 |
|
Slope |
0.0485 |
0.0153 |
|
Correlation coefficient (r) |
0.9994 |
0.9996 |
|
Accuracy (Mean ± SD) |
101.41 ± 0.59 |
100.36 ± 1.08 |
|
Precision (±%RSD) |
||
|
Repeatability |
101.81 ± 0.73 |
99.78 ± 1.14 |
|
Intermediate precision |
99.73 ± 0.88 |
99.55 ± 0.77 |
|
Specificity (Mean ± SD) |
100.85 ± 1.20 |
100.17 ± 1.02 |
II Method validation
All methods were validated according to ICH guidelines [17]. The linear regression data for the calibration curve showed good linear relationship (Table 1). The accuracy was calculated by analyzing the standard addition where satisfactory results were obtained as shown in (Table 1). The specificity of the method was calculated by assaying the laboratory prepared mixtures of PAR & ORP within the linearity range and good results were obtained (Table 1). The intra- and inter-day precisions were calculated by the analysis of 3 different concentrations of the drugs 3 times on the same day and on 3 successive days (Table 1).
III Application to Pharmaceutical Formulation
The proposed method was successfully applied for determination of PAR and ORP in their pharmaceutical formulation (Orphenadrine plus® tablets). The results were acceptable and with sufficient agreement with the labelled amounts. The standard addition technique was applied and showed that no interference of the excipients was observed (Table 2)..
Table 2: Analysis of the pharmaceutical preparation (Orphenadrine Plus® tablets) by applying Isoabsorptive assay method.
|
|
Isoabsorptive assay |
|||||||
|
ORP |
PAR |
|||||||
|
|
Recovery% |
|
Recovery% |
|||||
|
Tablet Taken (µg/mL) |
Standard Added (µg/mL) |
Tablet |
Added |
Tablet Taken (µg/mL) |
Standard Added (µg/mL) |
Tablet |
Added |
|
|
0.60 |
5 |
101.99 |
100.59 |
5.40 |
5 |
99.80 |
99.32 |
|
|
5.60 |
101.42 |
101.09 |
5.60 |
101.01 |
101.30 |
|||
|
6 |
100.82 |
100.87 |
6 |
98.59 |
99.88 |
|||
|
Mean |
|
|
101.41 |
100.85 |
|
|
99.80 |
100.17 |
|
SD |
|
|
0.59 |
0.25 |
|
|
1.21 |
1.02 |
IV Statistical Analysis
Statistical comparison of the proposed method was performed through One-way ANOVA method by using PASW statistics 18® software program in which there was no significant difference between the proposed method and the reference method [4] as shown in (Table 3).
Table 3: Statistical comparison of the results obtained by the proposed method and the reference method using One-way ANOVA.
|
Tablets |
Drugs |
|
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
Orphenadrine Plus ® tablets |
PAR |
Between Groups |
.077 |
1 |
.077 |
.040 |
.850 |
|
Within Groups |
7.619 |
4 |
1.905 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
7.697 |
5 |
|
|
|
||
|
ORP |
Between Groups |
2.522 |
1 |
2.522 |
1.716 |
.260 |
|
|
Within Groups |
5.880 |
4 |
1.470 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
8.402 |
5 |
|
|
|
Conclusion
Isoabsorptive point method was successfully applied for the determination of paracetamol and orphenadrine citrate in their binary mixtures and in their dosage form. The proposed method is simple, sensitive and accurate and could be used for routine analysis by using simple technology or instruments. By comparison with the previous reported methods, it was concluded that Isoabsorptive point method does not require extra processing but it may need a plateau region or a complementary technique for determination of one of the analytes. Statistical comparison revealed that there is no observed significant difference between the proposed method and the reference one.
Article Info
Article Type
Research ArticlePublication history
Received: Tue 03, Dec 2019Accepted: Thu 02, Jan 2020
Published: Mon 13, Jan 2020
Copyright
© 2023 Mahmoud Mohammed Mohammed Sebaay. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Hosting by Science Repository.DOI: 10.31487/j.GDT.2020.01.01
Author Info
Amr A. Mattar Mahmoud Mohammed Mohammed Sebaay
Corresponding Author
Mahmoud Mohammed Mohammed SebaayMedicinal Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Zagazig University, Zagazig 44519, Egypt
Figures & Tables
Table 1: Assay parameters and validation results obtained by applying Isoabsorptive assay spectrophotometric method.
|
Mixture |
PAR & ORP |
|
|
Method Parameters |
ORP |
PAR |
|
Wavelength (nm) |
211 |
280 |
|
Linearity range (µg/mL) (n=3) |
5-50 |
4-22 |
|
Intercept |
0.0427 |
0.0070 |
|
Slope |
0.0485 |
0.0153 |
|
Correlation coefficient (r) |
0.9994 |
0.9996 |
|
Accuracy (Mean ± SD) |
101.41 ± 0.59 |
100.36 ± 1.08 |
|
Precision (±%RSD) |
||
|
Repeatability |
101.81 ± 0.73 |
99.78 ± 1.14 |
|
Intermediate precision |
99.73 ± 0.88 |
99.55 ± 0.77 |
|
Specificity (Mean ± SD) |
100.85 ± 1.20 |
100.17 ± 1.02 |
Table 2: Analysis of the pharmaceutical preparation (Orphenadrine Plus® tablets) by applying Isoabsorptive assay method.
|
|
Isoabsorptive assay |
|||||||
|
ORP |
PAR |
|||||||
|
|
Recovery% |
|
Recovery% |
|||||
|
Tablet Taken (µg/mL) |
Standard Added (µg/mL) |
Tablet |
Added |
Tablet Taken (µg/mL) |
Standard Added (µg/mL) |
Tablet |
Added |
|
|
0.60 |
5 |
101.99 |
100.59 |
5.40 |
5 |
99.80 |
99.32 |
|
|
5.60 |
101.42 |
101.09 |
5.60 |
101.01 |
101.30 |
|||
|
6 |
100.82 |
100.87 |
6 |
98.59 |
99.88 |
|||
|
Mean |
|
|
101.41 |
100.85 |
|
|
99.80 |
100.17 |
|
SD |
|
|
0.59 |
0.25 |
|
|
1.21 |
1.02 |
Table 3: Statistical comparison of the results obtained by the proposed method and the reference method using One-way ANOVA.
|
Tablets |
Drugs |
|
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
Orphenadrine Plus ® tablets |
PAR |
Between Groups |
.077 |
1 |
.077 |
.040 |
.850 |
|
Within Groups |
7.619 |
4 |
1.905 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
7.697 |
5 |
|
|
|
||
|
ORP |
Between Groups |
2.522 |
1 |
2.522 |
1.716 |
.260 |
|
|
Within Groups |
5.880 |
4 |
1.470 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
8.402 |
5 |
|
|
|
References
- Yehia AM, Abd El Rahman MK (2015) Application of normalized spectra in resolving a challenging Orphenadrine and Paracetamol binary mixture. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 138: 21-30. [Crossref]
- Beebe FA, Barkin RL, Barkin S (2005) A clinical and pharmacologic review of skeletal muscle relaxants for musculoskeletal conditions. Am J Ther 12: 151-171. [Crossref]
- SratthaphutT L, Ruangwises N (2007) Determination of Paracetamol and Orphenadrine Citrate in Pharmaceutical Tablets by Modeling of Spectrophotometric Data Using Partial Least-Squares and Artificial Neural Networks. Yakugaku Zasshi 127: 1723-1729. [Crossref]
- Akshatha HS, Gurupadayya BM, Raikar PP (2018) Validated Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Orphenadrine Citrate and Paracetamol in Tablets by Simultaneous Equation Method. Int J ChemTech Res 11: 45-55.
- Nejem L, Antakli S, Bagdashe H (2013) Spectrophotometric determination of paracetamol and orphenadrine citrate in tablet. Asian J Chem 25: 1079-1082.
- Sharaf El Din MK, Abuirjeie MA, Abdel Hay MH (1991) Simultaneous Determination of Acetaminophen with Orphenadrine Citrate, Ibuprofen or Chlorzoxazone in Combined Dosage forms by Zero-Crossing Derivative Spectrophotometry. Analyt Lett 24: 2187-2206.
- Sebaiy MM, El Adl SM, Mattar AA (2020) Different techniques for overlapped UV spectra resolution of some co-administered drugs with paracetamol in their combined pharmaceutical dosage forms. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 224: 117429. [Crossref]
- Alfeen MA, Elias B, Al Ahmad Y (2017) Simultaneous Determination of Orphenadrine Citrate and Paracetamol in Tablets by using RP- HPLC Coupled with UV Detection. Chem Mater Res 9: 28-35.
- Samson Israel D, Krishna Chaitanya K, Gowri Sankar D, Vijayalakshmi A ()2013 Method development and validation for simultaneous determination a multiple drug dosage form of Paracetamol, Orphenedrine, Ibuprofen by RP-HPLC. J Glob Trend Pharmaceut Sci 4: 1153-1162.
- Nazir A, Naseer Y, Raza S, Shahid R (2016) Development & Validation of Analytical Method Used for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol , Caffeine and Orphenadrine Citrate By Hplc , in Pharmaceutical. Sci Int 28: 5215-5218.
- Sultana N, Arayne MS, Ali SN, Zuberi MH (2011) Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol and Orphenadrine Citrate in Dosage Formulations and in Human Serum by RP-HPLC. Med Chem Res 21: 2443-2448.
- Koppala Srinivasarao, Parsharamulu Rayam (2013) TLC-spectrodensitometric and microemulsion RP-HPLC chromatographic methods for determination of orphenadrine and paracetamol. Analyt Chem Indian J 13: 69-76.
- Eisele APP, Clausen DN, Tarley CRT, Dall’Antonia LH, Sartori ER (2013) Simultaneous Square-Wave Voltammetric Determination of Paracetamol, Caffeine and Orphenadrine in Pharmaceutical Formulations Using a Cathodically Pretreated Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Electroanalysis 25: 1734-1741.
- Lotfy HM, Tawakkol SM, Fahmy NM, Shehata MA (2014) Successive spectrophotometric resolution as a novel technique for the analysis of ternary mixtures of pharmaceuticals. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 121: 313-32yable3. [Crossref]
- Moussa BA, Mahrouse MA, Fawzy MG (2018) Different resolution techniques for management of overlapped spectra: Application for the determination of novel co-formulated hypoglycemic drugs in their combined pharmaceutical dosage form. Spectrochimica Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 205: 235-242. [Crossref]
- Lotfy HM, Mohamed D, Mowaka S (2015) A comparative study of smart spectrophotometric methods for simultaneous determination of sitagliptin phosphate and metformin hydrochloride in their binary mixture. Spectrochimica Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 149: 441-451. [Crossref]
- ICH. (2005)(Validation of Analytical Procedure: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1)). ICH Steering Committee 1994 (October 1994): 13.
