Transanal Evisceration in Rectal Perforation: Typical Presentation of a Rare Condition
A B S T R A C T
Transanal evisceration resulting from rectal perforation is a rare but potentially fatal event, if not treated promptly. We describe the case of an elderly woman for which the history of rectal prolapse played a major role in the etiopathogenesis of the event, undoubtedly. A surgical resection of the rectum was performed, with good results and without complications. Early recognition of this condition is necessary in order to treat it promptly with a surgical operation and lower morbidity and mortality rates.
Keywords
Transanal, evisceration, rectal perforation
Introduction
Rectal perforation with consequent transanal evisceration of the small bowel is a rare, but severe condition. Since the first case described by Brodie in 1827, few other cases have been described in the literature [1]. It represents a dramatic event with generally spontaneous onset and unclear pathogenesis, in which a chronic ischaemic insult to the rectal wall, resulting in thinning and subsequent perforation leads to transanal evisceration. Promptly surgical intervention, consisting of primary suture repair of the rectal tear or a Hartmann’s procedure is essential to minimize patient morbidity and mortality.
Case Presentation
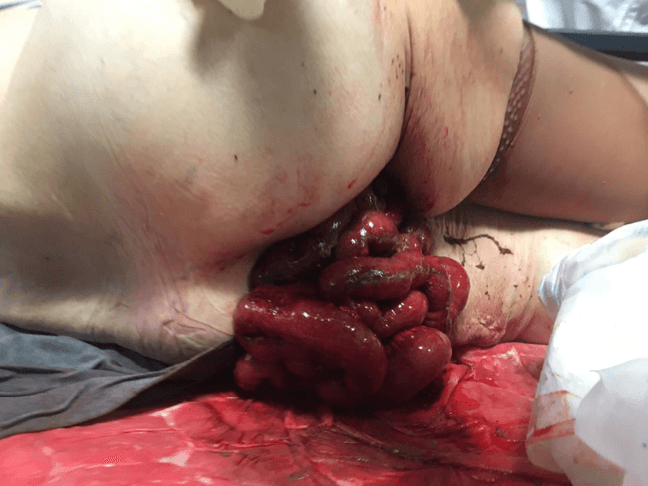
We present the case of a 65-year-old woman who was admitted to our Emergency Department with mild lower abdominal pain and transanal prolapse of the bowel. She was haemodynamically stable (blood pressure 160/60 mmHg; heart rate 86 bpm; respiratory rate 20/min). She had history of HCV infection, peripheral neuropathy and rectal prolapse. On examination, there was almost all the bowel protruding through the anus and the loops were oedematous and hypoperfused (Figure 1). Blood test revealed Hb 13.4 g/dL and WBC 12.1 × 109/L. At urgent laparotomy there was a fecal peritonitis. All the bowel was retracted through the anus and it was vital with no signs of ischaemia or perforation. Nevertheless, there was a large laceration of the intraperitoneal anterior rectal wall. Therefore, the operation was completed with rectal resection and Hartmann’s procedure with terminal colostomy. Open abdomen with negative pressure therapy (OA-NPT) was applied for 7 days because of the severe contamination. Abdomen definitive closure was achieved on post-operative day 8. The remaining course was uneventful. The patient was treated with broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics and discharged home on post-operative day 16.
Figure 1: The figure shows the oedematous and dusky eviscerated bowel loops.
Discussion
Rectal rapture with bowel evisceration is an uncommon surgical emergency with less than 100 cases in literature [2]. It is usually associated with long history of rectal prolapse, representative of the main recognized risk factor for this disease [3, 4]. Some studies describe this as a sliding hernia with the pouch of Douglas as sac. According to this theory, the Douglas pressure on the rectum make it weaker because of frequent ischaemic episodes [5]. In fact, histology of the rectum showed chronic inflammatory and ischaemic changes around the perforation site in almost 50% of patients. Other factors associated with a higher incidence of this event are mostly represented by history of constipation, iatrogenic causes or closed or penetrating trauma [6-10]. The coexistence of gynaecological pathologies or simply female sex were also more commonly found in these patients. However, a trigger is not always recognized [11, 12]. In our case, history of rectal prolapse certainly favoured the onset of transanal evisceration. Early surgical treatment with resuscitation and urgent operation resulted in a favourable outcome for the patient, avoiding nefarious consequences.
Statements and Declarations
The corresponding author declares that he acts on behalf of all authors and that all authors have approved the submission.
Data Availability
Information was obtained consulting clinical records but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Funding
None.
Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Copyright and Permissions
No pictures or parts of text reproduced or copied from other publications (including publications by the authors) are included in the manuscript.
Ethical Considerations
The study was based on hospital data obtained consulting clinical records, therefore ethical disclosure was not necessary.
Acknowledgments
Not necessary.
Article Info
Article Type
Case ReportPublication history
Received: Fri 24, Feb 2023Accepted: Mon 13, Mar 2023
Published: Thu 30, Mar 2023
Copyright
© 2023 Mauro Giambusso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Hosting by Science Repository.DOI: 10.31487/j.AJSCR.2023.01.05
Author Info
Valentina Bianchi Gaia Altieri Mauro Giambusso Antonio La Greca Marta Di Grezia
Corresponding Author
Mauro GiambussoEmergency and Trauma Surgery Unit, A. Gemelli University Hospital Foundation and IRCCS, Rome, Italy
Figures & Tables
References
1. Morris AM, Setty
SP, Standage BA, Hansen PD (2003) Acute transanal evisceration of the small
bowel: report of a case and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum
46: 1280-1283. [Crossref]
2. Hajiev S, Ezzat A,
Sivarajah V, Reese G, El-Masry N (2021) Transanal evisceration of small bowel
in two patients with chronic rectal prolapse: case presentation and literature
review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 103: e29-e34. [Crossref]
3. Cecilia M, Barambio
J, Escanciano M, Soares GS, Lopez OM et al. (2022) Rectal Prolapse and
Spontaneous Perforation Causing Transanal Evisceration of the Small Bowel: A
Case Report. Clinical History May Predict this Condition. Ann Case Report
7: 875.
4. Kornaropoulos M,
Makris MC, Yettimis E, Zevlas A (2016) Transanal evisceration of the small
bowel a rare complication of rectal prolapse. Int J Surg Case Rep 19:
38-40. [Crossref]
5. Furuya Y, Yasuhara
H, Naka S, Yamazaki K, Yanagie H et al. (2008) Intestinal evisceration through
the anus caused by fragile rectal wall. Int J Colorectal Dis 23
:721-722. [Crossref]
6. Lasheen O (2021)
Spontaneous trans-anal evisceration of small bowel: a case report. J Surg
Case Rep 18: rjaa582. [Crossref]
7. Hovey MA, Metcalf
AM (1997) Incarcerated rectal prolapse--rupture and ileal evisceration after
failed reduction: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 40: 1254-1257. [Crossref]
8. Narayana Swamy
Chetty YV, Sridhar M, and Pankaja SS (2014) Transanal evisceration of small
bowel-a rare surgical emergency. J Clin Diagn Res 8: 183-184. [Crossref]
9. Rechner P, Cogbill
TH (2001) Transanal small bowel evisceration from abdominal crush injury: case
report and review of the literature. J Trauma 50: 934-936. [Crossref]
10. Vincenzi R, Cruz RJ
Jr (2008) Transanal Small Bowel Evisceration: An Unusual Presentation of Rectal
Impalement. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 34: 606. [Crossref]
11. Pal AK, Kumar P, Yadav D, Kumar A, Pahwa HS et al. (2022) Spontaneous Rectal Perforation with Transanal Evisceration of the Small Bowel: A Rare Case Report. J Acute Care Surg 12: 74-76.
12. Walton SJ, Gobara O, Brown K (2013) Spontaneous transanal evisceration. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 95: 120-121. [Crossref]
